The Philippines' sprint towards a digital economy has been incredible, but it's a double-edged sword. While businesses are connecting and growing faster than ever, this very speed has exposed them to a growing number of cyber security issues. This digital gold rush has inadvertently made the country a prime hunting ground for cybercriminals, turning a massive opportunity into a significant risk for those who aren't prepared.
The New Digital Frontier and Its Dangers
Think of it like this: we've built a fantastic, modern city almost overnight, full of thriving businesses and bustling commerce. The only problem? We left the main gates wide open, with no guards on duty. That's a pretty good picture of the current cybersecurity situation in the Philippines.
The country's fast adoption of everything digital—from online shopping and banking to the massive shift to remote work—has simply outpaced the roll-out of solid security protocols. This gap between our technological leap forward and our security readiness has created a perfect storm.

For many businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), the main focus has understandably been on growth and keeping the lights on. Security often gets pushed to the back burner. Unfortunately, attackers know this and are quick to exploit these vulnerabilities. The very tools meant to help a business succeed—cloud services, online payment systems, and interconnected networks—can become unlocked doors for criminals if they aren't properly secured.
Understanding the Foundational Threats
When we talk about cyber security issues in the Philippines, it's easy to get lost in technical jargon. Let's cut through that. These aren't abstract problems; they're real-world events that can shut down your operations, empty your bank accounts, and shatter your company's reputation.
Here are the most common threats businesses are up against right now:
- Phishing: This is the classic con game, updated for the digital age. Attackers send fake emails that look like they're from your bank, a supplier, or even your own HR department. The goal is simple: trick an employee into giving up a password or financial detail. For example, an accountant might receive a fake email from "BDO" asking them to verify a transaction, leading them to a fake website that steals their login credentials. One click can give them the keys to your entire network.
- Ransomware: Imagine walking into your office and finding every single one of your files locked up—customer lists, financial records, everything. That's ransomware. It's a type of malicious software that holds your data hostage, demanding a huge payment to get it back. A practical example is a small logistics company in Manila getting hit and being unable to access their delivery schedules, bringing their entire operation to a standstill.
- Malware: This is a catch-all term for nasty software like viruses, spyware, and trojans. Each is designed to cause chaos, whether it's by disrupting your operations, corrupting your data, or secretly siphoning sensitive information straight to an attacker's server. For instance, spyware could be hidden in a "free" software download and secretly record every keystroke an employee makes, capturing passwords and sensitive company data.
For a Filipino business, a cyber attack isn't some far-off possibility—it's a clear and present danger. A single breach can cause a devastating domino effect: massive financial loss, serious penalties under the Data Privacy Act, and a loss of customer trust that can be impossible to win back.
Why Proactive Security Is a Business Imperative
Here’s the hard truth: cybercriminals are organised, they're well-funded, and they're constantly inventing new ways to attack. They specifically look for what they see as easy targets—companies without a dedicated IT security team or a solid defence plan.
Simply waiting for an attack to happen is a losing game. A proactive defence is the only way to ensure your business can survive and continue to grow. It’s also critical to keep up with how fast the threat landscape is changing, especially with the rise of AI-powered cyber threats that make attacks smarter and harder to detect.
Ultimately, tackling these challenges is a core business function, just as vital as sales, marketing, or finance. Protecting your digital assets is the same as protecting your bottom line. To get a wider perspective, you might be interested in our article on broader technological issues in the Philippines. In the sections that follow, we'll dig deeper into specific threats and give you actionable steps to fortify your defences.
What Cyber Threats Are Hitting Philippine Businesses the Hardest?
It’s one thing to talk about cyber risks in theory, but it’s another to see how they actually bring a business to its knees. The most common cyber security issues in the philippines aren't just technical glitches; they are direct threats that can stop your operations cold and drain your bank account.
Many of these attacks don't just brute-force their way in. They prey on the single most common vulnerability in any organisation: human error. Attackers have become masters of social engineering, using psychology to manipulate your staff into making simple but costly mistakes. Let's break down the threats that are causing the most damage right now.

Phishing: The Deceptive Lure
Phishing is still one of the most dangerously effective tactics in an attacker's playbook. Think of it as digital con artistry. The attacker sends an email or message that looks like it's from a legitimate source—a bank, a government agency, or even your own HR department.
A practical example of this is a spear-phishing attack, where an attacker researches a company's CEO and sends a fake email from their account to the finance department, urgently requesting a wire transfer to a new "supplier." This highly targeted approach makes it very convincing and has tricked many Filipino companies.
Ransomware: The Digital Hostage Crisis
Ransomware is a business owner's worst nightmare. This nasty piece of software gets into your network and encrypts everything you rely on: customer data, financial records, project files. Everything becomes completely inaccessible. Then comes the demand for a massive ransom, usually in cryptocurrency, in exchange for a key to get your data back.
A real-world example would be a private hospital in Quezon City suddenly finding all patient records, schedules, and billing systems encrypted. They can't admit new patients or access critical medical histories, forcing them to either pay a huge ransom or face a complete operational shutdown and potential lawsuits.
DDoS Attacks: Overwhelming Your Defences
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is like a digital mob blocking the entrance to your store. Attackers use a massive network of infected computers—a botnet—to flood your website or online services with so much junk traffic that it collapses under the strain, blocking actual customers from getting through.
For an e-commerce site or a hotel, a DDoS attack is a direct hit on your bottom line. A practical example is a popular local online retailer's website being flooded with traffic during the 11.11 sale, making it impossible for legitimate customers to make purchases and causing massive revenue loss.
This isn't a minor issue here. The Philippines has become a major target, partly due to geopolitical tensions. At one point, the nation was ranked 2nd globally for DDoS attacks in a single quarter. Overall, cyber incidents exploded by 300% between 2019 and 2022, revealing just how vulnerable many local systems are to malware and data leaks.
The Need for a Structured Defence
These examples show how attackers come at you from all angles—targeting your people, your data, and your infrastructure. To build a solid defence, you need a structured plan. A great starting point is the globally recognised OWASP Top Ten, which outlines the most critical security risks to web applications. Understanding these common weak points is the first step toward building a truly resilient business.
Why SMBs, BPOs, and Hotels Are Prime Targets
Cybercriminals aren’t just hunting for big, headline-grabbing corporate giants. Here in the Philippines, they’re often much smarter than that. They pick their targets carefully, focusing on industries where they can get the biggest payoff for the least amount of work. Knowing why your industry might be on their radar is the first real step to building a defence that actually works.
Three sectors pop up again and again: small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) centres, and hotels. Each one is a tempting prize for attackers, but for entirely different reasons. Let's break down what makes these businesses so attractive to them.
SMBs: The Path of Least Resistance
Many small and medium business owners fall into the trap of thinking, "We're too small to be a target." That’s a dangerous, and often expensive, assumption. The hard truth is, attackers don't just see SMBs as targets; they often see them as the best targets precisely because they’re easier to get into.
Think of it from the criminal's perspective. It's a business. They want to maximise their profit and minimise their effort. They know perfectly well that most SMBs are running lean, often without a dedicated IT security person or the kind of robust defences a large corporation would have. This makes them "low-hanging fruit"—vulnerable and ready to be picked.
A Real-World Scenario: The Ransomware Ripple Effect
Picture a small manufacturing company in Laguna. They don't have an IT team, and their idea of a backup is an external hard drive they plug in once a week. Someone clicks on a bad link in an email, and just like that, ransomware locks up their entire server—production schedules, client orders, everything. Now they face a terrible choice: pay a massive ransom they can't afford or lose weeks trying to rebuild from scratch, almost certainly losing key customers along the way.
BPOs: The Data Goldmines
The BPO industry is a pillar of the Philippine economy, but its greatest asset—its direct line to global client data—is also its biggest weakness. When attackers hit a BPO, they aren't just after the BPO's money. They're after the incredibly valuable information these centres hold for huge international companies.
BPOs are virtual goldmines, processing and storing millions of sensitive records. We're talking about everything from customer financial details and private healthcare information to a company's own secret sauce. A single successful breach of a Philippine BPO can have massive global ripple effects, which makes them a magnet for sophisticated, well-organised attackers.
- Valuable Client Data: BPOs handle it all, from credit card numbers for global retail brands to personal health records for insurance providers.
- A Gateway to Bigger Networks: Breaking into a BPO can give an attacker a trusted backdoor into the networks of their much larger, international clients.
- High-Pressure Environments: The fast-paced, high-volume nature of call centres can sometimes lead to small security slip-ups. Attackers are masters at spotting and exploiting these tiny cracks.
A Real-World Scenario: One Click Cripples an Operation
Imagine a large call centre in Cebu handling customer service for a European e-commerce giant. An agent, rushing between calls, opens a very convincing phishing email and accidentally installs spyware. The attackers stay quiet for weeks, secretly siphoning off customer login details and payment info. By the time they launch a massive fraud campaign, the client's reputation is in tatters and it’s become a major international incident.
Hotels: The Hubs of Transient Data
Hotels are in the business of making people feel welcome, but behind the scenes, they’re also in the business of data collection. Every single guest who checks in leaves behind a trail of personal and financial information. This creates a constantly refreshing pool of valuable data that’s incredibly tempting for cybercriminals. From the booking systems to the guest Wi-Fi, a hotel is a complex maze of technology with plenty of potential weak spots.
What attackers want from hotels is this transient data. A credit card number is only valuable for a short time before it gets cancelled. A steady stream of new card details from a hotel’s reservation system, however, is a highly profitable product on the dark web.
A Real-World Scenario: The Wi-Fi Honeypot
A beautiful boutique hotel in Palawan offers its guests free Wi-Fi. But the network isn't properly secured, allowing an attacker to sit in the lobby and set up a "man-in-the-middle" attack. They intercept everything—banking app logins, social media passwords, and corporate emails from dozens of international tourists. The hotel might not find out for months, but the reputational damage from a flood of negative online reviews can cause bookings to plummet.
What a Major Security Breach Really Costs a Business
It’s one thing to know that hackers are targeting certain industries, but it’s another thing entirely to live through the fallout of an attack. When a security breach happens, it stops being a theoretical risk on a spreadsheet and becomes a full-blown crisis that can bring a company to its knees. These incidents aren't just IT problems; they are catastrophic events that have severe, long-lasting consequences for the entire business.
Looking at major local cybersecurity incidents, you can see the devastating domino effect a single breach has. The damage goes far beyond the initial panic, triggering operational, financial, and legal nightmares that can drag on for years. All of a sudden, a company's focus shifts from growth and innovation to pure damage control.
The Immediate Grind to a Halt
The very first thing that happens in a serious breach is a crippling operational shutdown. When attackers unleash ransomware or take over your core systems, business doesn't just slow down—it stops. This isn’t a minor hiccup; it’s a hard stop on your ability to make money.
A practical example is a chain of retail stores finding its point-of-sale (POS) system completely frozen by malware. They cannot process any credit card or e-wallet payments, forcing them to turn away customers and losing an entire day's sales across all branches.
The image below shows which sectors in the Philippines are prime targets and the valuable data they protect—the very data that, if compromised, leads to these kinds of shutdowns.
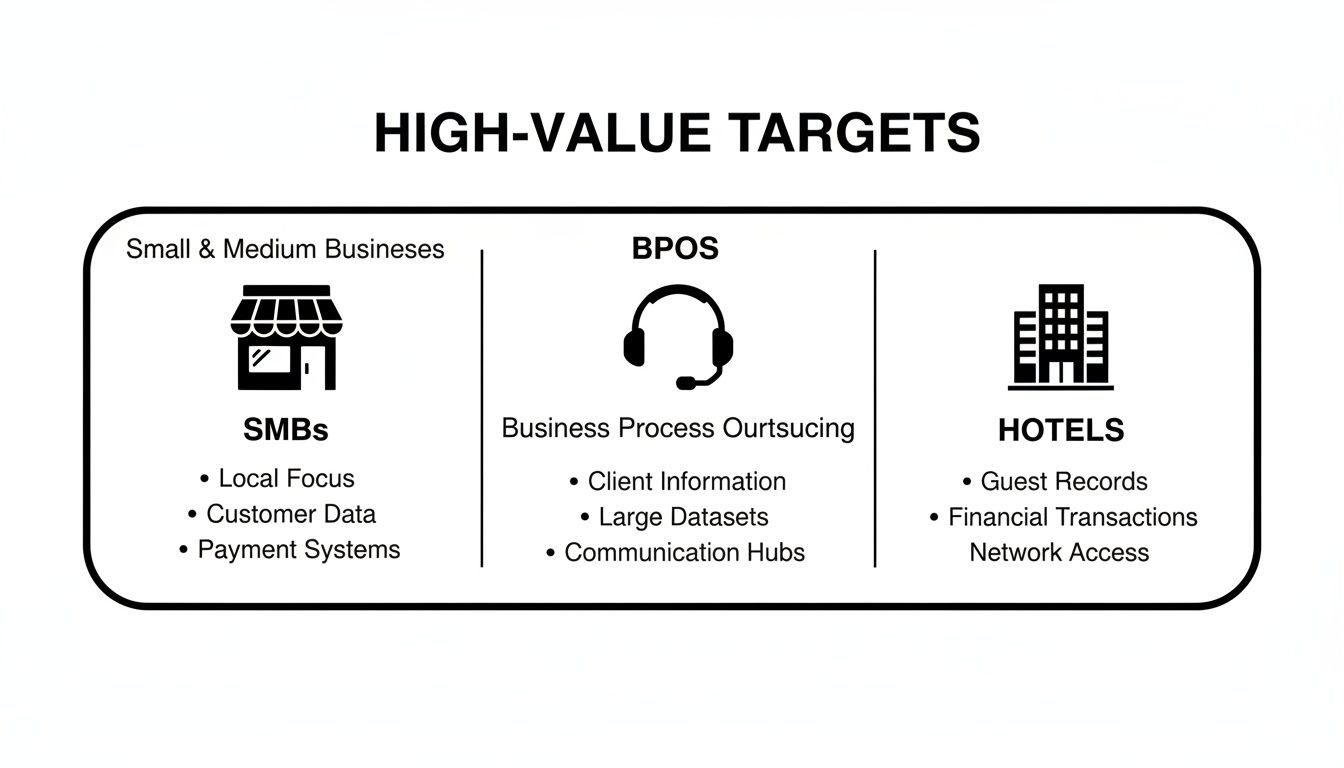
Whether it's an SMB's customer list, a BPO's client database, or a hotel's payment records, this data is the lifeblood of the business. Losing access to it is catastrophic.
The Aftermath: Financial Bleeding and a Ruined Reputation
Once operations are frozen, the financial bleeding starts almost immediately. The costs tied to a breach are staggering and come from all directions.
- Recovery Costs: This bucket includes everything from hiring expensive forensic experts to figure out what happened, to completely rebuilding your IT systems from the ground up.
- Regulatory Fines: If your company is found non-compliant with the Data Privacy Act, you could be facing substantial penalties. A security failure quickly becomes a very costly legal disaster.
- Reputational Damage: This is often the most painful and long-lasting consequence. Trust is built over years but can be shattered in an instant. When customers find out their personal data has been exposed, they often leave and never come back.
A data breach isn't just a one-time expense. It’s an ongoing financial drain that eats away at profits and investor confidence, often leading to a permanent loss of market share.
The scale of this problem is staggering. A recent survey revealed that 84% of organisations in the Philippines experienced at least one cybersecurity breach in the past year, with an average of over 3.13 incidents per company. This places the country among the top ten most targeted nations for sophisticated attacks like AI-powered phishing and ransomware-as-a-service.
Breaches like the massive PhilHealth incident exposed the sensitive data of millions, serving as a harsh wake-up call for organisations to invest in better security, including robust backup systems. You can learn more about the different types of backup solutions in our detailed guide.
Anatomy of a Data Breach: The Business Impact
To really understand the full scope of the damage, it helps to break down the consequences. The table below illustrates the direct and indirect costs that a typical Philippine business faces after a security incident.
| Impact Area | Description of Consequence | Example for a Philippine Business |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Financial Loss | Immediate costs incurred to contain and remediate the breach, including ransom payments, IT forensics, and system restoration. | A retail chain paying millions of pesos to a ransomware group and hiring a cybersecurity firm to rebuild its point-of-sale system. |
| Regulatory Penalties | Fines imposed by the National Privacy Commission (NPC) for violations of the Data Privacy Act (DPA) of 2012. | An online lender being fined for failing to protect customer financial data, a penalty that can reach up to ₱5 million. |
| Operational Downtime | Lost revenue and productivity from the inability to conduct normal business operations while systems are offline. | A logistics company's delivery network is paralysed for days, unable to track shipments or coordinate with drivers, leading to huge losses. |
| Customer Churn | Loss of existing customers who no longer trust the business with their personal information following a breach. | A hotel group losing loyal patrons after their booking information and payment details were leaked online. |
| Brand & Reputation Damage | Long-term harm to the company's public image, making it difficult to attract new customers, partners, and even employees. | A BPO losing a major international client because it can no longer be trusted to handle sensitive customer data securely. |
| Legal & Litigation Costs | Expenses related to lawsuits filed by affected customers, partners, or regulatory bodies. | A financial institution facing a class-action lawsuit from clients whose personal and banking information was compromised. |
As you can see, the impact goes far beyond the IT department. A single breach creates ripples that affect every part of the organisation, from finance and legal to sales and marketing, for years to come.
Getting to Grips with the Data Privacy Act
If you’re doing business in the Philippines, you absolutely have to know the lay of the land when it comes to data protection. This isn’t just a recommendation; it’s a legal must-do. At the heart of it all is the Data Privacy Act of 2012 (R.A. 10173), a serious piece of legislation built to safeguard the personal information of Filipinos. Getting this wrong isn't a simple oversight—it can bring down a world of hurt on your business.
Think of the Data Privacy Act (DPA) as the official rulebook for handling personal data, whether it belongs to your customers or your own staff. It’s not about making data useless by locking it away. It’s about being responsible and respectful—making sure you collect, use, and store information the right way.
Let’s be clear: ignoring these rules is a massive gamble. The penalties for non-compliance are severe. We're talking about hefty fines that can climb as high as ₱5 million, and in the worst cases, actual prison time for company leadership. Suddenly, data protection stops being just an IT problem and becomes a major boardroom issue.
What the Law Actually Expects From You
Staying compliant with the DPA means more than just slapping a privacy policy on your website and calling it a day. It demands real, practical steps to weave a security-first mindset into your company's DNA. The law lays out a few non-negotiable duties for every business, no matter how big or small.
Here’s a breakdown of your core responsibilities:
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): This person is your go-to expert and advocate for data privacy internally. They're in charge of your compliance plan, oversee security efforts, and act as your official liaison with the National Privacy Commission (NPC).
- Run Privacy Impact Assessments: You need to regularly check how your operations could affect people's privacy. A practical example is an e-commerce company assessing the privacy risk of a new feature that collects user location data to offer targeted promotions.
- Implement Solid Security Measures: The DPA requires you to have the right mix of organisational, physical, and technical safeguards in place. This covers everything from locking down your servers and controlling who can access data to training your employees on how to handle sensitive information properly.
A small hotel in Boracay, for instance, has a legal duty to protect its guest registration forms—the ones with names, addresses, and phone numbers. This means no leaving forms out on the counter, keeping digital records on encrypted, password-protected systems, and shredding paper copies when they're no longer needed. If that data gets stolen because of carelessness, the hotel owner could be looking at both huge fines and a lawsuit.
The True Price of Getting It Wrong
The penalties under the DPA are designed to make you pay attention. A breach that happens because you didn't follow the rules can set off a chain reaction of disasters that go way beyond the government fines.
Imagine a BPO that cuts corners on its security. A data breach exposes the sensitive client information it was paid to protect. Here’s the fallout they’re facing:
- NPC Investigation and Fines: The National Privacy Commission will be all over it, and the financial penalties that follow can be crushing.
- Loss of Client Contracts: The international clients whose data was leaked? They're almost guaranteed to pull their business, causing a massive, potentially fatal, drop in revenue.
- Civil Lawsuits: The people whose data was exposed can sue for damages, piling on even more legal fees and payouts.
- Criminal Liability: If it's found that the breach happened due to gross negligence, the company's directors could face jail time. That’s a career-ending, life-changing outcome.
Successfully navigating these regulations isn’t a one-and-done job. It’s an ongoing commitment to protecting the trust people place in you and your business, and it’s the only way to stay on the right side of the law.
Building Your Practical Business Defence Plan
Knowing about the cyber security threats here in the Philippines is one thing, but it’s not enough. To really protect your business, you have to move from just spotting problems to actively building a real-world defence. A solid security posture isn't about a single, perfect wall; it’s about creating layers of protection that all work together to keep intruders out.
This means putting together a strategy that marries good technology with smart processes and, most crucially, people who are prepared. Let's break down the essential pieces of a defence plan that any Filipino organisation can start putting into practice today.
Fortifying Your Digital Perimeter
Your network is essentially the digital front door to your business. If you leave that door unlocked, you're just asking for trouble. The very first layer of your defence should be hardening this perimeter to make it as tough as possible for anyone unauthorised to get in.
Here’s where you start:
- Configuring Firewalls Correctly: Think of a firewall as the security guard for your network. It checks everything coming in and going out, blocking anything that looks shady or breaks the security rules you've set. A practical example is setting up a rule to block traffic from countries where you don't do business, reducing the surface area for attacks.
- Securing Your Wi-Fi: An open Wi-Fi network is a huge, flashing vulnerability. You absolutely must use strong encryption (like WPA3), hide your network name (SSID), and set up a completely separate guest network for visitors. This stops them from ever touching your core business systems.
Practical Example: A BPO in Manila can create a separate guest Wi-Fi network for visitors and applicants. This simple step ensures that a visitor's potentially infected personal laptop cannot be used as a jumping-off point to attack the company’s internal servers, where sensitive client data is stored.
Building Your Human Firewall
Let's be clear: technology on its own will never be enough. Your employees are your first and most important line of defence, but without proper training, they can also be your weakest link. Transforming your team into a "human firewall" is one of the smartest, most cost-effective security investments you'll ever make.
This isn't about a one-off orientation session. It's about building a real culture of security awareness through ongoing training. You want security to be a reflex for your team, not an afterthought.
A Real-World Scenario: A small hotel group starts running quarterly phishing simulations. They send out fake but believable emails to staff—things like a phony "Urgent Invoice" or a "Reset Your Password" request. When an employee clicks the fake link, instead of a virus, they get a short training module. After six months, the number of employees falling for the simulations drops by over 70%.
Planning for the Worst-Case Scenario
No defence is foolproof. Even with the best preparation, a breach can still happen. The difference between a business that survives an attack and one that doesn't often comes down to having a clear plan before disaster strikes. An Incident Response Plan (IRP) is your step-by-step emergency playbook.
This plan needs to answer some critical questions long before you're in a crisis:
- Who’s in charge? You need to designate a clear incident response leader. For example, in a small business, this might be the owner or the most tech-savvy manager.
- How do we stop the bleeding? Lay out the immediate steps to contain the breach, like disconnecting affected systems from the network.
- Who do we tell? Establish protocols for notifying management, employees, clients, and legal bodies like the National Privacy Commission.
- How do we get back online? Document the procedures for restoring data from backups and safely bringing systems back into operation.
Having this plan ready means you can act fast and with purpose, which dramatically minimises the damage and downtime. For businesses looking to build a truly comprehensive strategy, exploring professional cyber security solutions can offer the expert guidance needed to create a resilient defence.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to cybersecurity, it's easy to feel like you're staring at a mountain of technical jargon. For busy business owners, finding a clear path forward can be tough. Here are some straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often from businesses across the Philippines.
Where Do I Even Begin with Cybersecurity?
The best place to start is with a simple question: What am I trying to protect? You can't secure everything at once, so begin by identifying your most critical digital assets. This could be your customer database, your financial records, or the sensitive intellectual property that keeps you ahead of the competition.
Once you know what’s most valuable, you can focus your efforts. A few practical first steps include:
- Making sure everyone uses strong, unique passwords.
- Turning on two-factor authentication (2FA) on every account that offers it. For example, requiring a code from a phone app in addition to a password to log into company email.
- Keeping all your software and systems updated—those updates often contain critical security patches.
Is Professional Cybersecurity Too Expensive for a Small Business?
That’s a very common concern, but it often frames the problem the wrong way. Think about the potential cost of a breach: the lost sales from downtime, the fines from regulators, and the long-term damage to your reputation. Suddenly, proactive defence looks a lot more affordable.
Investing in cybersecurity isn't just another business expense; it's a core function that protects your ability to operate. The real question isn't whether you can afford security, but whether your business can survive without it.
Many IT providers now offer managed security services that are specifically designed to scale with a small or medium-sized business's budget, giving you professional-grade protection without the enterprise price tag.
What Is the Single Most Effective Security Measure I Can Take?
Technology like firewalls and antivirus software is absolutely essential, but if you had to pick just one thing, it would be employee training. Your team is your first and last line of defence—a human firewall.
Time and again, we see that training your staff to spot phishing emails, use strong passwords, and follow security best practices stops the vast majority of attacks before they can ever touch your technical systems. A practical example is training them to hover over links in emails to see the actual web address before clicking, a simple habit that can foil many phishing attempts.
How Does the Data Privacy Act Affect My Business?
If you collect any kind of personal information from customers or employees—we're talking names, addresses, phone numbers, anything that can identify a person—then the Data Privacy Act of 2012 applies to you. It's not optional.
The law legally obligates you to implement reasonable security measures to protect that data. Failing to do so can lead to massive fines and, in serious cases, even imprisonment for company officers. Compliance isn’t just good practice; it's a legal necessity.
Protecting your business from today's cyber threats requires a partner who understands the local landscape. REDCHIP IT SOLUTIONS INC. delivers managed IT and security services that keep your operations safe and resilient. Learn more about our solutions at redchipcomputers.com.





